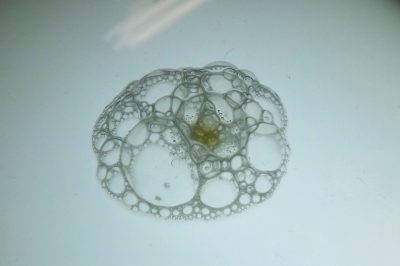
Catalase test
Published 03/29/2012
(Authors: David Torrens González, Marta Martín García).
The image shows the “bubbling” that occurs when a drop of 30% hydrogen peroxide is poured onto an isolated colony of the Staphylococcus aureus organism. This bubbling is a consequence of the action of an enzyme called catalase that, when in contact with hydrogen peroxide, converts this compound into water and oxygen. This enzyme is only possessed by certain microorganisms. The catalase test is an enzymatic test used for the identification of numerous microorganisms.